Import Google Spreadsheet
Description
Import specific worksheets from Google Spreadsheet files.
Examples
No examples yet...
Import Parameters
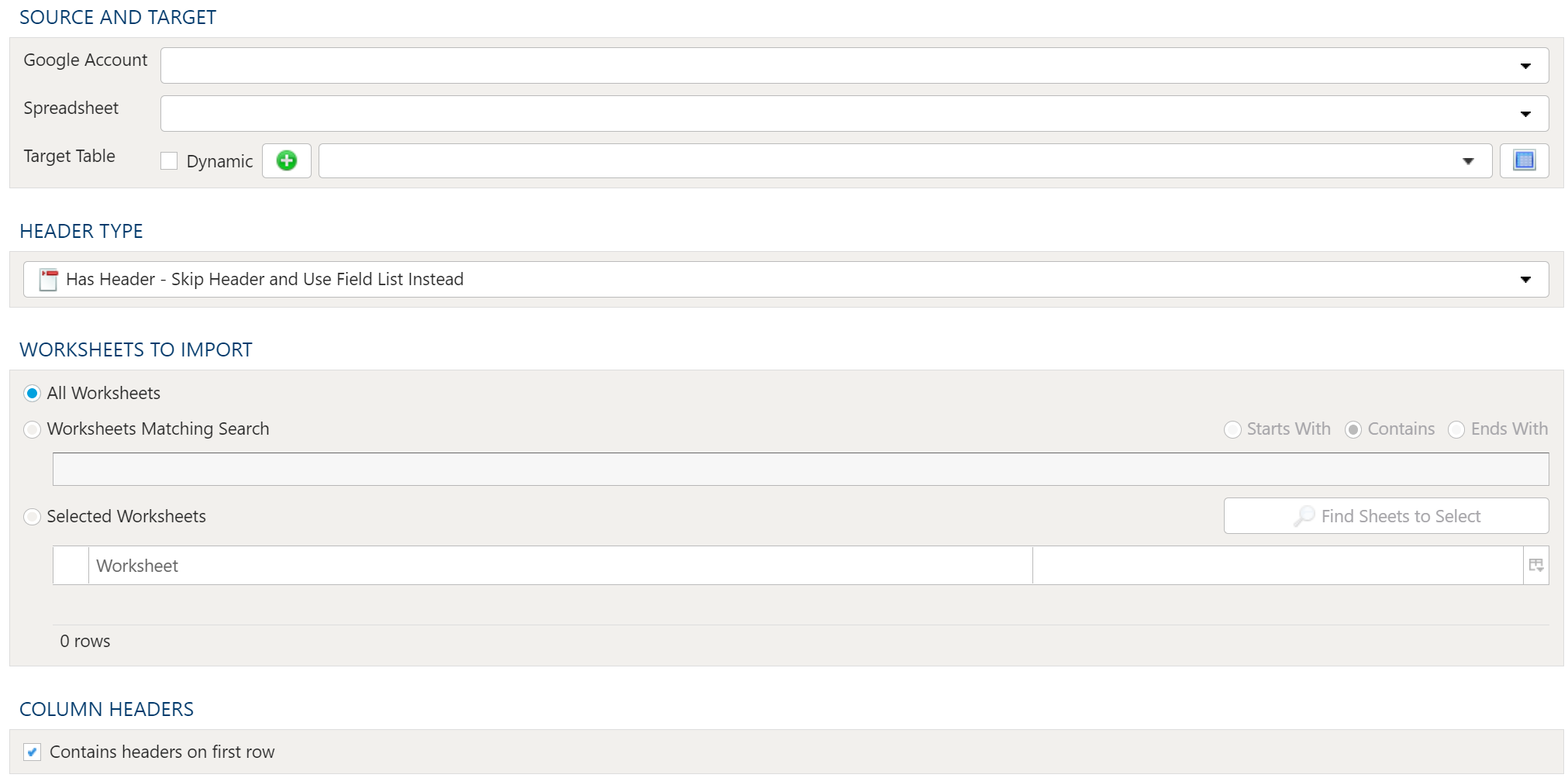
Source And Target
Google Account
Accessing Google Spreadsheet data requires a valid Google user account. This requires set up in Tools. For details on setting up a Google account connection, see here: PlaidCloud Tools – Connection.
Once all necessary accounts have been set up, select the appropriate Google Account from the drop down list.
Spreadsheet
Next, specify the Spreadsheet to import from the dropdown menu containing all available files associated with the specified Google Account.
Target Table
The target selection for imports is limited to tables only since views do not contain underlying data.
Dynamic Option
The Dynamic option allows specification of a table using text, including variables. This is useful when employing variable driven workflows where table and view references are relative to the variables specified.
An example that uses the current_month variable to dynamically point to target table:
legal_entity/inputs/{current_month}/ledger_values
Static Option
When a specific table is desired as the target for the import, leave the Dynamic box unchecked and select the target Table.
If the target Table does not exist, select the Create new table button to create the table in the desired location.
Table Explorer is always avaible with any table selection. Click on the Table Explorer button to the right of the table selection and a Table Explorer window will open.
Header Type
Since Google Spreadsheets may or may not contain headers, PlaidCloud provides a way to either use the headers, ignore headers, or use column order to determine the column alignment.
- No Header: The file contains no header. Use the source list in the Data Mapper to determine the column alignment
- Has Header - Use Header and Override Field List: The file has a header. Use the header names specified and ignore the source list in the Data Mapper.
- Has Header - Skip Header and Use Field List Instead: The file has a header but it should be ignored. Use the header names specified by the source list in the Data Mapper.
Worksheets to Import
Because workbooks may contain many worksheets with different data, it is possible to select which worksheets should be imported in the current import process. The options are:
- All Worksheets
- Worksheets Matching Search
- Selected Worksheets
Using Worksheet Search
The search functionality for worksheets allows inclusion of worksheets matching the search criteria. The search criteria allows for:
- Starts With: The worksheet name starts with the search text
- Contains: The worksheet name contains the search text
- Ends With: The worksheet name ends with the search text
Find Sheets in Selected File
The find sheets button will open the Excel file and list the worksheets available in the table. Mark the checkboxes in the table for the worksheets to be included in the import.
Column Headers
Table Data Selection
Data Mapper Configuration
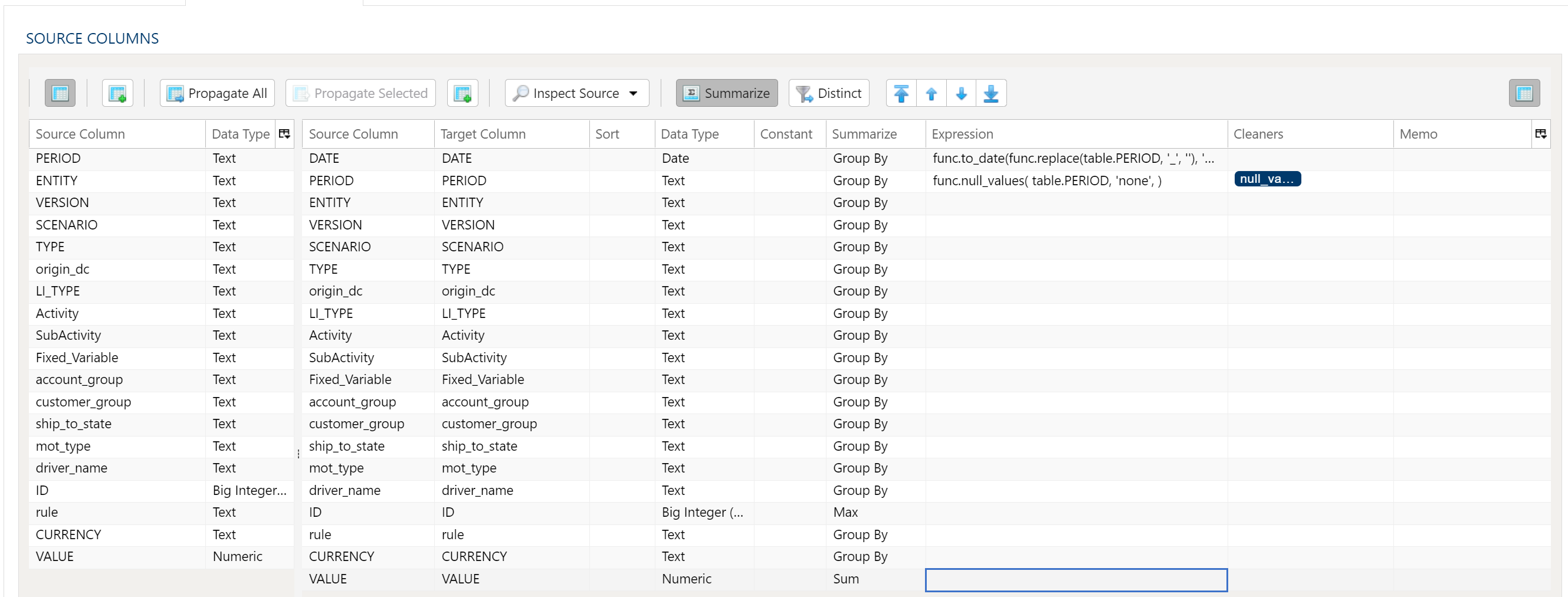
The Data Mapper is used to map columns from the source data to the target data table.
Inspection and Populating the Mapper
Using the Inspect Source menu button provides additional ways to map columns from source to target:
- Populate Both Mapping Tables: Propagates all values from the source data table into the target data table. This is done by default.
- Populate Source Mapping Table Only: Maps all values in the source data table only. This is helpful when modifying an existing workflow when source column structure has changed.
- Populate Target Mapping Table Only: Propagates all values into the target data table only.
If the source and target column options aren’t enough, other columns can be added into the target data table in several different ways:
- Propagate All will insert all source columns into the target data table, whether they already existed or not.
- Propagate Selected will insert selected source column(s) only.
- Right click on target side and select Insert Row to insert a row immediately above the currently selected row.
- Right click on target side and select Append Row to insert a row at the bottom (far right) of the target data table.
Deleting Columns
To delete columns from the target data table, select the desired column(s), then right click and select Delete.
Changing Column Order
To rearrange columns in the target data table, select the desired column(s). You can use either:
- Bulk Move Arrows: Select the desired move option from the arrows in the upper right
- Context Menu: Right clikc and select Move to Top, Move Up, Move Down, or Move to Bottom.
Reduce Result to Distinct Records Only
To return only distinct options, select the Distinct menu option. This will toggle a set of checkboxes for each column in the source. Simply check any box next to the corresponding column to return only distinct results.
Depending on the situation, you may want to consider use of Summarization instead.
The distinct process retains the first unique record found and discards the rest. You may want to apply a sort on the data if it is important for consistency between runs.
Aggregation and Grouping
To aggregate results, select the Summarize menu option. This will toggle a set of select boxes for each column in the target data table. Choose an appropriate summarization method for each column.
- Group By
- Sum
- Min
- Max
- First
- Last
- Count
- Count (including nulls)
- Mean
- Standard Deviation
- Sample Standard Deviation
- Population Standard Deviation
- Variance
- Sample Variance
- Population Variance
- Advanced Non-Group_By
For advanced data mapper usage such as expressions, cleaning, and constants, please see the Advanced Data Mapper Usage
Data Filters
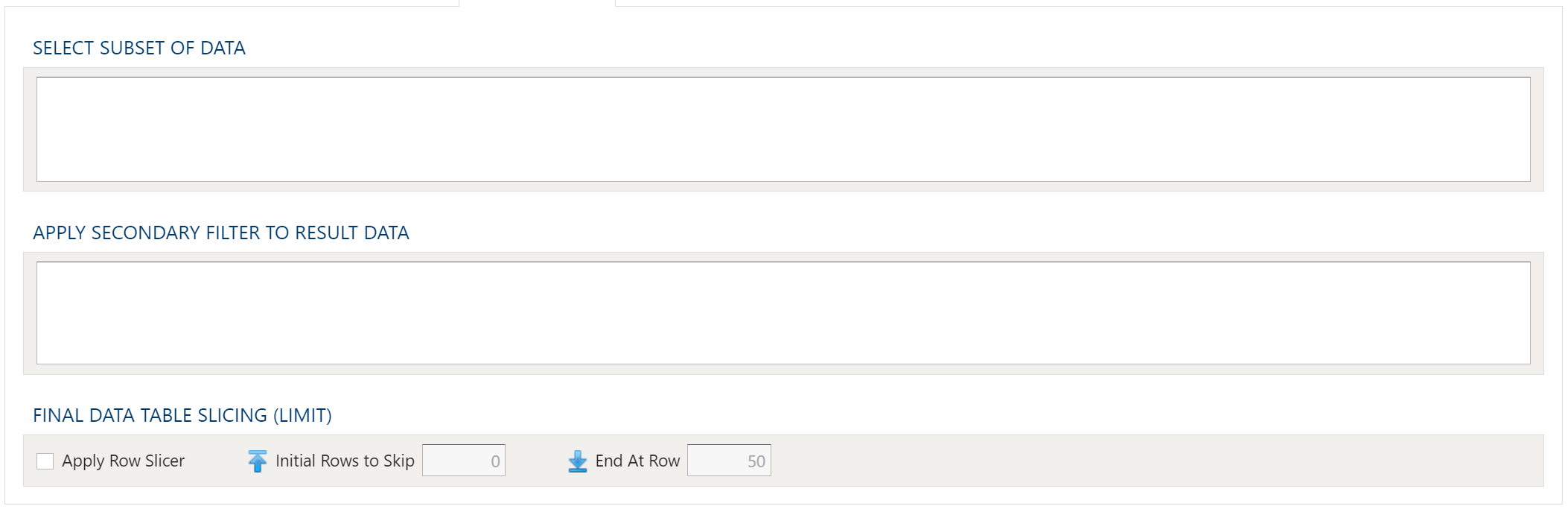
To allow for maximum flexibility, data filters are available on the source data and the target data. For larger data sets, it can be especially beneficial to filter out rows on the source so the remaining operations are performed on a smaller data set.
Select Subset Of Data
This filter type provides a way to filter the inbound source data based on the specified conditions.
Apply Secondary Filter To Result Data
This filter type provides a way to apply a filter to the post-transformed result data based on the specified conditions. The ability to apply a filter on the post-transformed result allows for exclusions based on results of complex calcuations, summarizaitons, or window functions.
Final Data Table Slicing (Limit)
The row slicing capability provides the ability to limit the rows in the result set based on a range and starting point.
Filter Syntax
The filter syntax utilizes Python SQLAlchemy which is the same syntax as other expressions.
View examples and expression functions in the Expressions area.